World's First Fourth Generation Nuclear Plant Expansion Begins
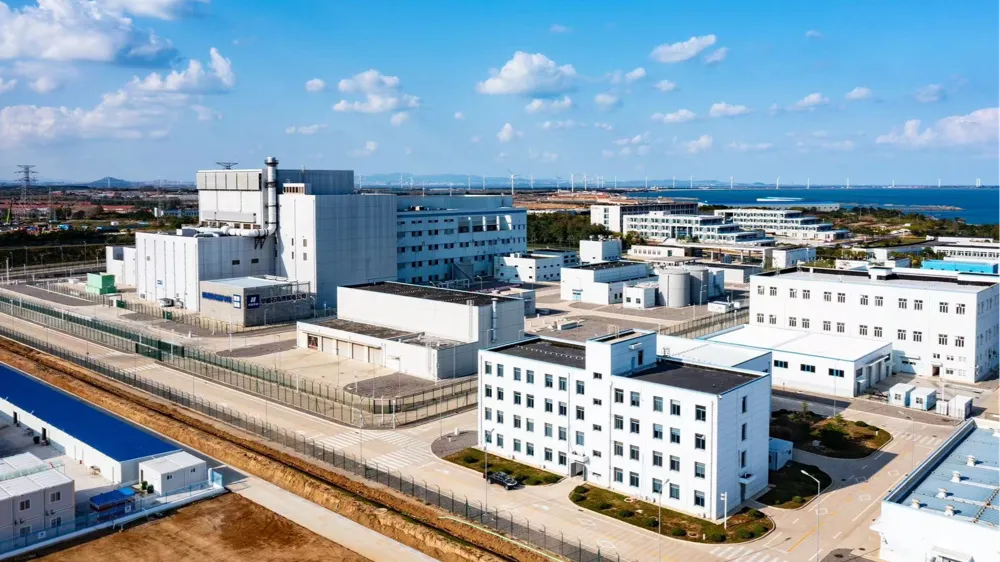

The expansion of the world's first fourth-generation nuclear power plant, the Shidaowan high-temperature gas-cooled reactor nuclear power plant, commenced in east China's Shandong Province on Sunday, marking a significant step forward in China's commitment to increasing its clean energy capacity.
Located in Rongcheng County, Weihai City, the Shidaowan project is notable for being developed entirely with Chinese intellectual property rights. It is a collaborative effort involving China Huaneng Group, Tsinghua University, and China National Nuclear Corporation.
The facility, which features the world's first high-temperature gas-cooled reactor, began commercial operations in December last year. This cutting-edge technology underscores China's advancements in nuclear technology and its ambition to lead in the global energy transition.
As part of the first phase of the expansion, plans include the installation of an additional domestically developed third-generation pressurized water reactor known as Hualong One. According to Zhang Aijun, vice president of HTGR Nuclear Power Company, Ltd, this reactor will operate in conjunction with the existing gas-cooled reactor.
Zhang stated that the initial phase involves two units of the Hualong One reactors, each boasting a capacity of 1.2 million kilowatts. Once fully operational, the plant is expected to generate 20 billion kilowatt-hours annually and expand its heating supply area by 20 million square meters, benefiting around 600,000 residents.
Future phases of the expansion will see the addition of four more pressurized water reactors, each with a capacity exceeding one million kilowatts. This will significantly enhance the plant's overall capability.
Upon completion of the entire expansion plan, the total installed capacity of the power plant will surpass five million kilowatts, with an anticipated annual generation capacity of 35 billion kilowatt-hours. This output will be sufficient to cater to the electricity needs of over 17 million households annually.
The environmental benefits are notable; the expansion is projected to offset approximately 11.5 million tonnes of standard coal consumption and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by around 27.6 million tonnes each year.
Zhang emphasized the importance of maximizing the effectiveness of both the third-generation pressurized water reactors and the fourth-generation high-temperature gas-cooled reactors at the facility. This strategic integration aims to advance China's capabilities in nuclear power equipment and its comprehensive utilization.
This expansion not only solidifies China's position in nuclear technology but also plays a crucial role in fostering new and high-quality productive forces within the sector. As the world shifts toward sustainable energy solutions, the Shidaowan project exemplifies a proactive approach to addressing energy consumption and environmental challenges.
Read These Next
Nvidia's $5B Investment in Intel: Semiconductor Implications
This article discusses Nvidia's recent $5 billion investment in Intel and its implications for the semiconductor industry amid growing demands for AI technology.

UK Analysis Attributes 10% of China's Growth to Clean Energy
Clean-energy tech contributed over 10% to China's GDP in 2024, with $950 billion in investments, outpacing traditional sectors.
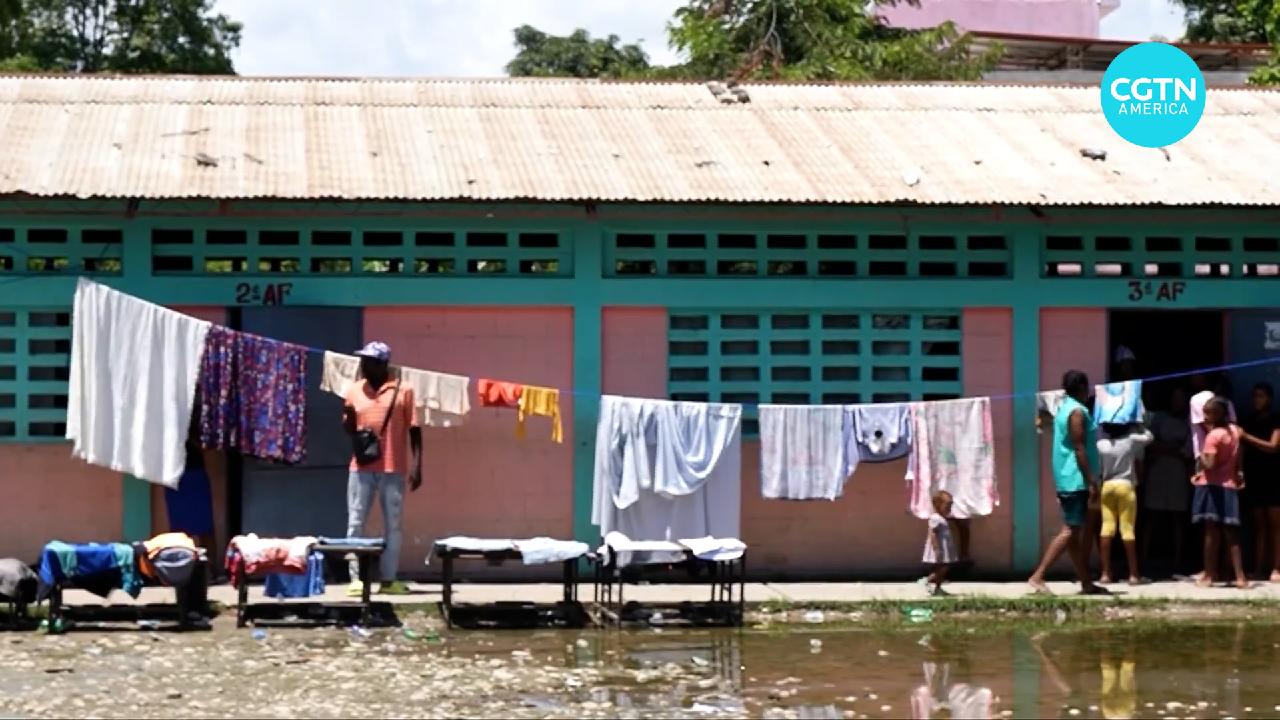

Haiti Faces Health Emergency as Gang Violence Intensifies
Gang violence in Haiti worsens health emergency, impacting healthcare access and raising safety concerns for medical assistance.
