3D DRAM Technology Breakthrough Announced
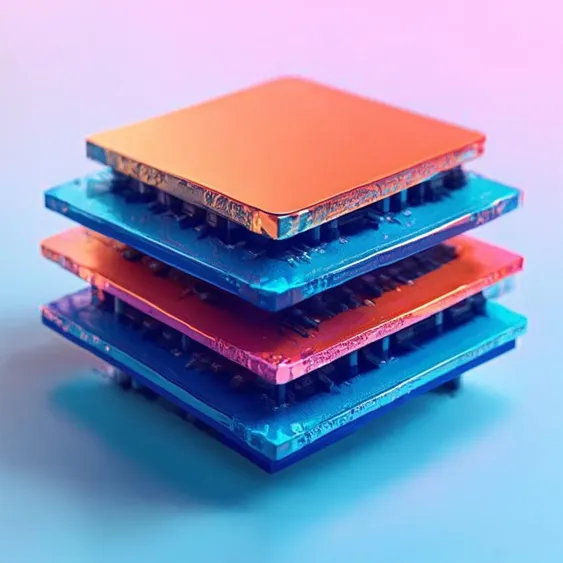

The recent breakthrough reported by Imec and Ghent University in developing a 120-layer 3D DRAM structure using alternating layers of silicon and silicon-germanium is a significant milestone in memory technology. As the demand for high-capacity storage continues to rise, this development offers promising avenues for enhancing DRAM performance, much like the transformational impact 3D NAND architectures have had on solid-state drives (SSDs). Moving forward, the efficiency gains in DRAM will be critical for a variety of applications, ranging from data centers to consumer electronics, where performance and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
The traditional 2D DRAM architecture has served well for decades, but the increasing requirements for data speed and storage density have necessitated innovation. The adoption of 3D structures, similar to advancements in NAND flash, allows for more memory cells to be compacted into a smaller footprint. In the case of the newly developed structure, researchers have achieved over 100 stacked layers, representing a significant step towards overcoming the limitations of current DRAM designs. Each layer's composition is meticulously controlled—65nm silicon and 10nm silicon-germanium layers alternate to create a dense and efficient architecture, which is key for boosting storage density.
The implications of this technology extend beyond mere performance improvements. As the semiconductor industry grapples with physical limitations in miniaturization, the ability to stack components vertically allows for a continuation of Moore's Law in a different form. By leveraging techniques such as low-pressure chemical vapor deposition and addressing defect minimization effectively, researchers are paving the way for mass production of high-density DRAM, with significant potential to lower costs per gigabyte and improve yields.
The successful implementation of this 3D DRAM structure raises significant questions about the future of memory technologies: will we see a complete transition from 2D to 3D designs? How quickly can the industry adapt to these advancements, and what will be the cost implications for manufacturers? As the landscape of computing continues to evolve, it will be interesting to observe how this technology integrates into existing paradigms and fuels further innovations in memory solutions.
Read These Next
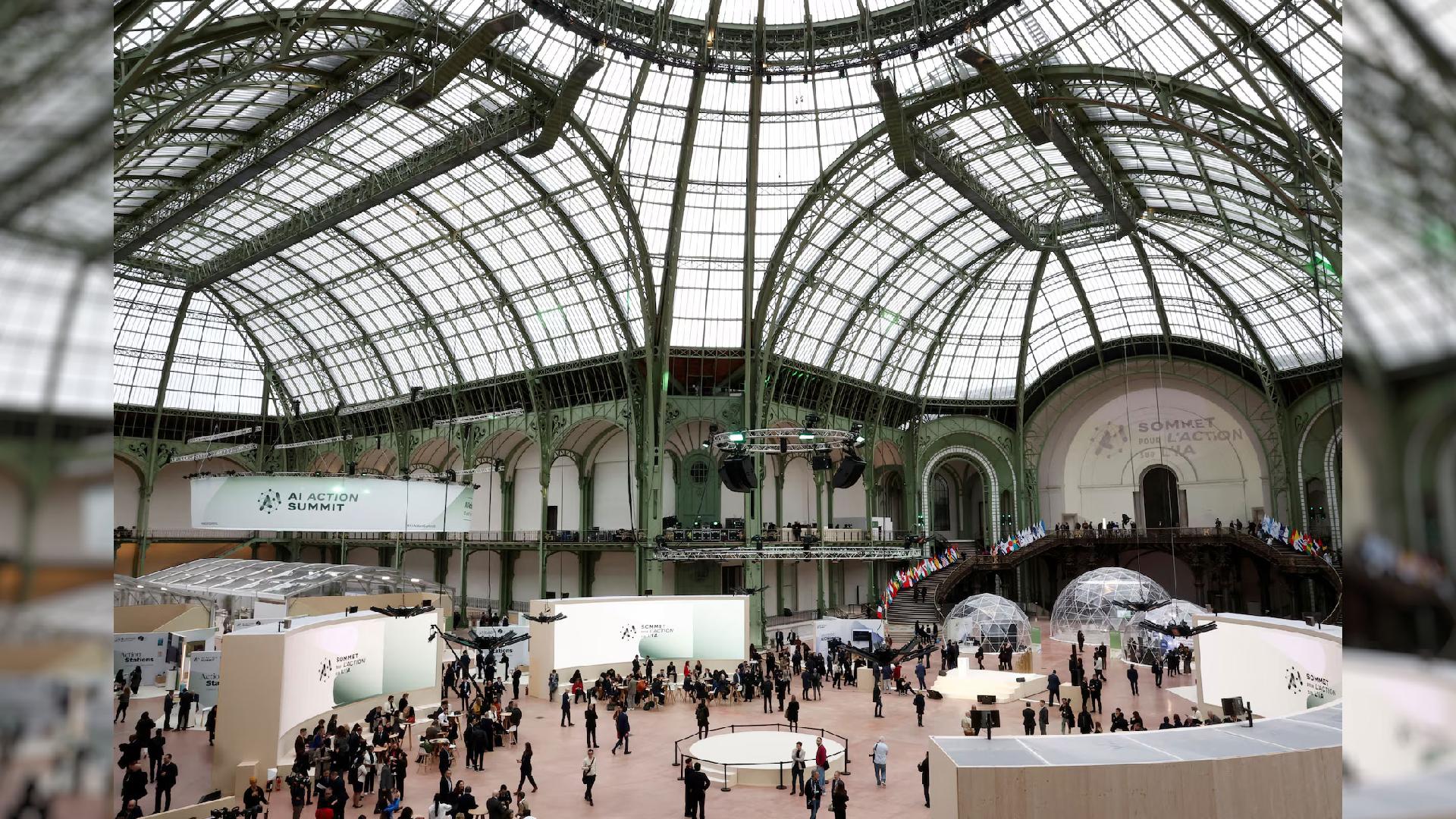

Global Leaders and Tech CEOs Unite in Paris for AI Summit
A summit in Paris addressed AI innovation and responsibility, emphasizing the need for international cooperation and regulation.

China Calls on US to Avoid Politics in COVID-19 Origins Probe
China urges the US to halt political maneuvering on COVID-19 origins, emphasizing transparency and international collaboration.
Moon Soil Samples to be Featured at World Expo 2023
Moon soil samples from China’s Chang'e-6 mission will be showcased together for the first time at World Expo 2025 in Osaka.
