Companies Targeting Elimination of Forever Chemicals

The issue of harmful substances known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), colloquially termed "forever chemicals," has garnered significant attention due to their persistence in the environment and concerning health effects. As these chemicals do not break down easily, they accumulate in our soil and water systems, raising alarms over potential exposure leading to serious health issues, including various cancers and reproductive problems. Understanding how to effectively eliminate PFAS is crucial not only for public health but also for environmental restoration, particularly as regulations tighten worldwide.
PFAS are synthetic chemicals designed for specific properties, such as water and grease resistance, leading them to be utilized in items ranging from non-stick cookware to packaging for food. Their strong carbon-fluorine bonds make them robust and stable, resulting in a slow degradation rate that keeps them in our ecosystems for years. Current methods of dealing with PFAS concentrate on either long-term storage or incineration, both of which come with risks, either due to potential leakage or the production of toxic byproducts. However, innovative technologies are emerging to tackle this problem head-on. For instance, electrolytic oxidation utilizes electricity to break down PFAS in contaminated water, offering a method that, while energy-intensive, integrates smoothly into existing treatment facilities. Similarly, supercritical water oxidation can decompose these chemicals under extreme boiling conditions, effectively dismantling the stable bonds. Although these technologies have shown promise in pilot projects, they also entail their own set of challenges, particularly regarding cost and the management of any harmful byproducts that may arise during the decomposition process.
In summary, the elimination of PFAS stands at a critical juncture where scientific innovation meets urgent environmental necessity. As technologies like electrolytic oxidation and supercritical water oxidation advance, they pave the way for more effective management of PFAS contamination. However, careful consideration of their implications, including potential byproducts and costs, remains essential. Interested readers can explore further by examining resources from environmental organizations, research institutions, or initiatives led by government agencies such as the U.S. Department of Defense, which is spearheading projects aimed at PFAS remediation.
Read These Next
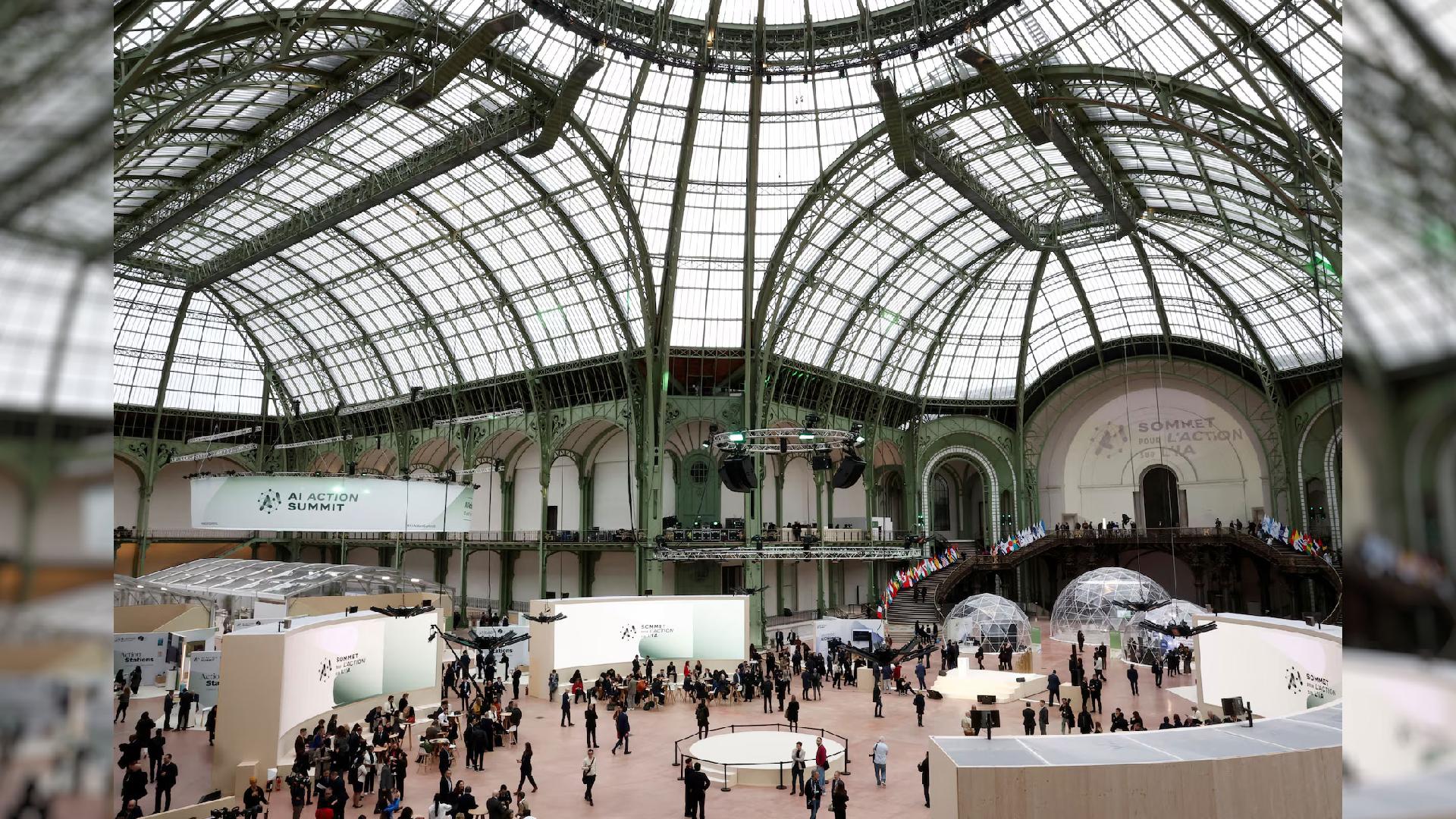

Global Leaders and Tech CEOs Unite in Paris for AI Summit
A summit in Paris addressed AI innovation and responsibility, emphasizing the need for international cooperation and regulation.

China Calls on US to Avoid Politics in COVID-19 Origins Probe
China urges the US to halt political maneuvering on COVID-19 origins, emphasizing transparency and international collaboration.
Moon Soil Samples to be Featured at World Expo 2023
Moon soil samples from China’s Chang'e-6 mission will be showcased together for the first time at World Expo 2025 in Osaka.
