China unveils new technique for mass-producing quality semiconductors
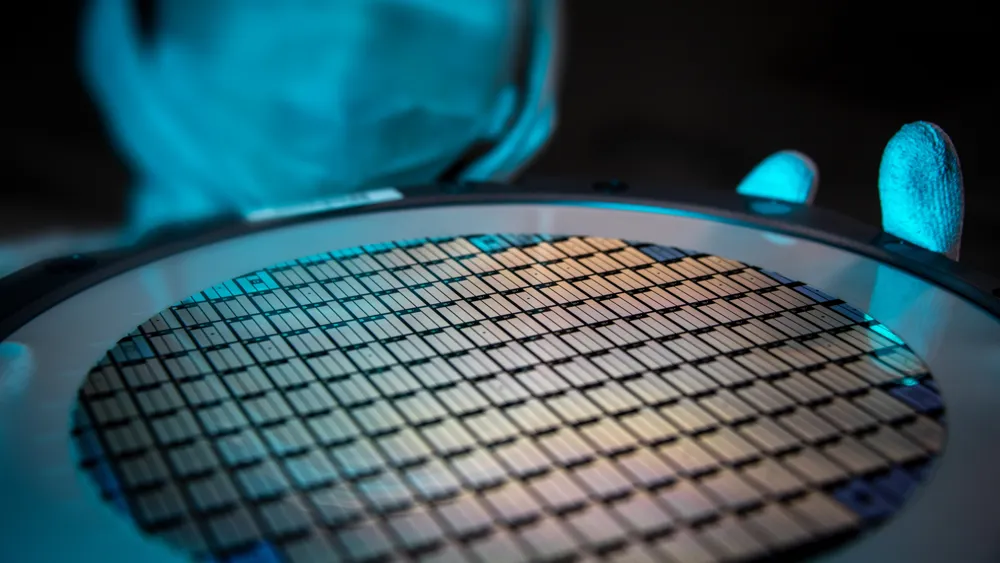
Chinese scientists have made significant strides in semiconductor technology by devising a novel method for the mass production of high-quality indium selenide, which is being hailed as a potential game changer in the manufacturing of advanced chips.
The groundbreaking study, recently published online by the scientific journal Science, was carried out by a collaborative research team from Peking University and Renmin University of China.
Integrated circuits, essential to modern information technology, face performance limitations as traditional silicon-based chips approach their physical boundaries. Therefore, there is a pressing global focus on developing high-performance, energy-efficient semiconductor alternatives.
Indium selenide, often referred to as a 'golden semiconductor,' has long been sought after for its advantages. However, the challenge of producing it at scale in high quality has previously limited its application.
According to Liu Kaihui, a professor at Peking University's School of Physics, the primary obstacle has been ensuring the precise maintenance of the ideal 1:1 atomic ratio of indium to selenium during production.
In tackling this challenge, the research team employed an innovative technique that involved heating an amorphous indium selenide film and solid indium within a sealed environment. The process allowed vaporized indium atoms to form an indium-rich liquid interface at the film's edge, enabling the gradual production of high-quality indium selenide crystals characterized by a regular atomic structure.
This new methodology not only maintains the correct atomic ratio but also alleviates a major bottleneck in the journey of indium selenide from laboratory settings to practical engineering applications.
The technical advancements achieved by the team include the successful production of indium selenide wafers measuring 5 centimeters in diameter and the construction of large arrays of high-performance transistors, which are primed for direct application in integrated chip devices, as noted by researcher Qiu Chengguang.
Liu emphasized that this breakthrough paves the way for the next generation of high-performance, low-power chips, which are anticipated to become fundamental in fields such as artificial intelligence, autonomous driving, and smart technology.
The innovative work has received acclaim from reviewers of Science, who have recognized it as a significant advancement in the field of crystal growth.
Read These Next

Dual Black Holes Merging with Third Dense Body: Commentary
A critical commentary on the recent discovery regarding binary black holes merging near a third dense object, its implications, and significance in astrophysics.

Meta's Profit Surge Fuels Ambitious AI Projects
This article discusses how Meta Platforms is leveraging its surge in profits to invest in ambitious AI projects, driven by CEO Mark Zuckerberg's vision for superintelligence. The piece highlights the impact of these developments on Meta's strategy and the broader technology landscape.
China achieves first brain-computer interface experiment on human
Nankai University completed the first interventional brain-computer interface experiment on a human, enhancing motor functions for paralysis.
