China's Role in Enhancing Global Immunity Efforts
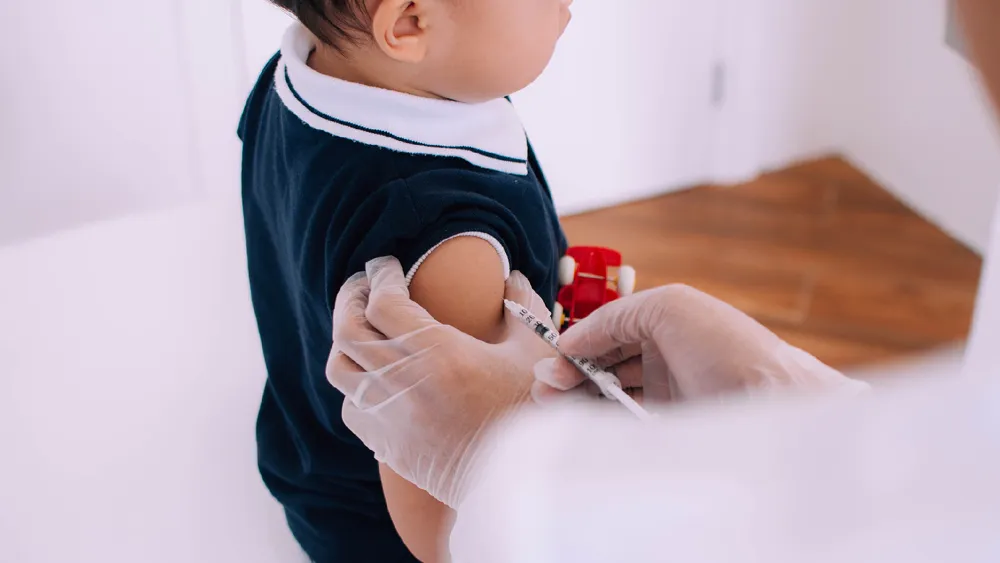
China's immunization programs have taken center stage in global health discussions, particularly highlighted on World Strengthened Immunity Day. Celebrated annually on December 15, this day aims to enhance awareness about the critical role of immunization in safeguarding against vaccine-preventable diseases while promoting public health through effective vaccination programs.
First established by the World Health Organization in 1988, World Strengthened Immunity Day was originally a response to the urgent need for international collaboration to eliminate polio, a disease that predominantly impacts young children and can result in permanent paralysis.
The significance of this day lies not only in raising awareness but also in underlining the necessity of vaccines to impede the propagation of infectious diseases. It highlights the essential collective actions required to sustain high immunity levels within populations around the globe.
Immunity, a vital physiological function regulated by the immune system, involves the detection and elimination of foreign pathogens and the management of damaged cells, including those associated with tumors. Vaccines represent one of the most economically efficient strategies to avert the transmission of infectious maladies.
In 2024, the global health community will observe the 50th anniversary of the Expanded Programme on Immunization, an initiative that, according to the WHO, has saved over 154 million lives worldwide, with China playing a pivotal role in this achievement.
Since its immunization program was launched in 1978, China has successfully prevented more than 300 million cases of vaccines-preventable diseases such as polio, diphtheria, and hepatitis B. This significant transformation has seen China evolve from being predominantly a recipient of vaccines to becoming a key donor, thus protecting both its citizens and contributing to global health efforts.
China's commitment to immunization is further evident by its incorporation of the hepatitis B vaccine into its national childhood immunization agenda since 2002, achieving over 90 percent coverage among newborns. This positions China among the frontrunners in implementing comprehensive immunization initiatives.
Epidemiologist Feng Zijian noted the tangible impacts of vaccination rates, reporting a continual decline in disease incidence, with more than a 95 percent reduction observed in numerous targeted illnesses. Notably, diphtheria has been nearly eradicated in China over the past two decades.
The framework supporting China's immunization program is fortified by legislative measures and a robust vaccine management strategy. The enactment of the 2019 Vaccine Administration Law has established a solid legal foundation for regulating the vaccine industry.
Since the implementation of the national immunization program, there has been a remarkable decrease of over 99 percent in the incidence of seven out of fifteen targeted diseases included in China's expanded immunization program, a testament to the efficacy of vaccines in combating infectious diseases.
Read These Next

Wuhan University Decodes Jupiter's Magnetosphere and Europa
Wuhan University's breakthrough in understanding Jupiter's magnetosphere interactions with Europa sheds light on planetary science and cosmic phenomena.
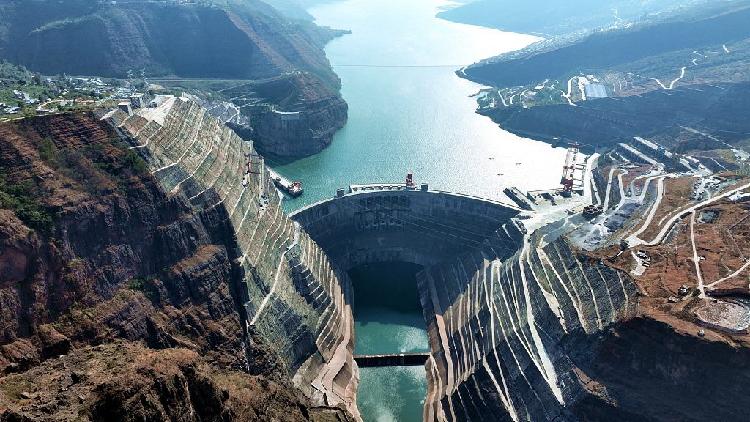

Baihetan Hydropower Station Marks Two Years of Clean Energy Progress
Baihetan Hydropower Station aids China's clean energy shift, reducing coal use and emissions with advanced hydropower technology.
Commentary on 'Microwave Brain' Tech Development
Commentary on the groundbreaking 'microwave brain' technology that integrates AI and communication chips, discussing its innovations and implications for future technologies.
