China's DeepSeek and Its Global AI Impact
In late January 2024, the launch of China's DeepSeek-R1 app sent shockwaves through the tech industry, particularly in Silicon Valley. This artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot quickly surpassed other popular apps like ChatGPT and raised questions about China's position in the global AI landscape. DeepSeek's impressive performance not only erased a staggering $600 billion in market value from chip manufacturer Nvidia, but it also challenged the longstanding belief that bigger and costlier AI models guaranteed superior quality. Understanding the implications of DeepSeek is crucial, as it signifies a potential shift in how AI development is approached and perceived in both the US and China.
So, what exactly is DeepSeek and how does it work? Essentially, DeepSeek-R1 is a large language model (LLM) that utilizes algorithms to predict the next word in a sentence, enabling it to generate coherent responses in human-like conversations. The revelation that DeepSeek was developed with significantly fewer resources than its American competitors, costing around $5.6 million compared to the billions spent by companies like OpenAI, shed light on efficiency. This efficiency lets startups leverage high-performing AI at lower costs. As businesses scrambled to adopt DeepSeek, some even devised methods to run the model on personal devices, seeking to enhance data privacy over concerns regarding user data being stored on Chinese servers.
In conclusion, DeepSeek represents a critical juncture in the AI race, showcasing that innovation can emerge from unexpected sources and challenging preconceived notions about resource requirements. While the initial excitement around DeepSeek seems to have stabilized, its effect on the industry persists, pushing developers to rethink strategies around model efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the landscape remains uncertain, leaving one to ponder: can smaller, less resource-intensive models redefine the future of AI? For those interested in AI trends and implications, following emerging models and their adaptability could provide valuable insights into the industry's trajectory.
Read These Next
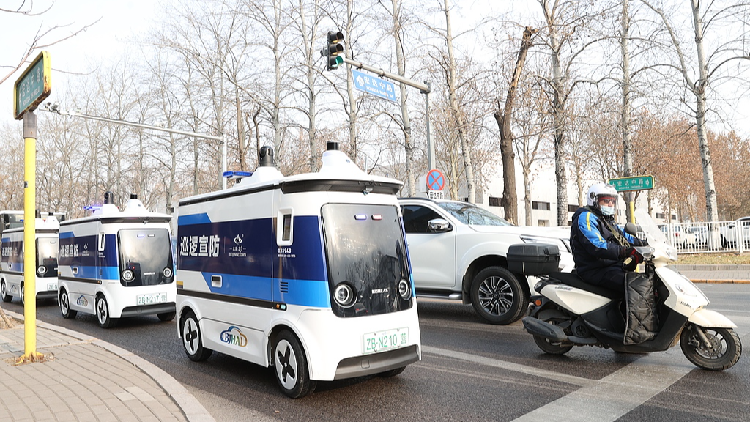

Beijing to Create 3000 Square Kilometer Autonomous Driving Zone
Beijing plans a 3,000-sq-km autonomous driving zone to boost tech innovation and improve urban mobility efficiency and safety.

Expert Highlights Global Competitiveness of China's New Three
Zhang Jianping evaluates China's foreign trade in new energy vehicles, lithium-ion batteries, and photovoltaics, showcasing its dominance.

Helium-3 on Moon: Interlune and Astrolab Partner Up
Interlune's partnership with Astrolab aims to explore helium-3 mining on the Moon, highlighting opportunities for clean energy production while raising ethical considerations regarding space resource extraction.
